Constructions (non-transparent)
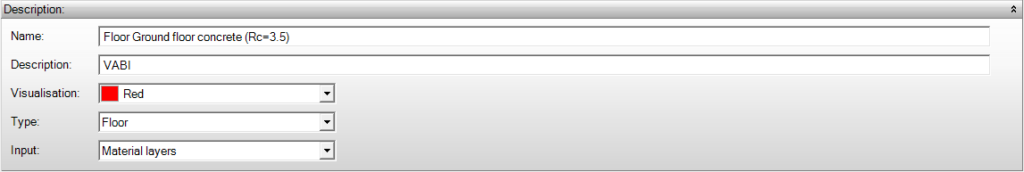
Description
Name and Description
Provide a recognizable name and any description so that you can easily find the constructions.
Visualisation
A construction can be visualized using a color. In Properties – building parts, you can use this to clearly identify your components in the table and in the 3D model.
Type
The construction types are automatically recognized by the program in a geometry and can be automatically assigned in a architectural template:
- Floor: Automatically assigned to all lower surfaces of spaces. A distinction is made between intermediate floors and floors that border outside air or ground.
- Flat Roof: Automatically assigned to all upper horizontal surfaces that border outside air. If the surface is not horizontal, it is automatically classified as a sloped surface.
- Sloping Roof: Automatically assigned to all upper diagonal surfaces that border outside air. If the surface is horizontal, it is automatically classified as a flat roof.
- Wall or Partition Walls: Automatically assigned to all vertical or nearly vertical surfaces of a space. We distinguish between internal walls and walls that border outside air. These walls can be either load-bearing or non-load-bearing.
- Panel: Automatically assigned to all placed panels. You place these sub-surfaces yourself in the Geometry.
- Window: Automatically assigned to all placed windows. You place these sub-surfaces yourself in the Geometry.
- Door: Automatically assigned to all placed doors. You place these sub-surfaces yourself in the Geometry.
Which constructions should be automatically assigned can be specified in the architectural template.
Input
This determines how the construction is specified and calculated. A construction is specified using material layers or based on Rc-value and mass.
- Material Layers: With this option, you specify a construction using a set of predefined materials. The Rc- or U-value of the entire construction is then automatically calculated for you based on the current standards. For this option, materials must be defined.
- Rc and Density: With this option, you specify an Rc-value yourself. This means a simplified calculation, which can be useful if the materialization is not yet known. For this option, you do not need to define materials.
- Normal Window: When the window type is selected, you can choose the input data for a normal window.
- Climate Window: When the window type is selected, you can choose the input data for a climate window. This includes inner and outer glass data, and possible ventilation. As with the standard window, you can also specify the frame data and possible sun shading.
For Building Simulation, it is mandatory to specify the construction using material layers.
In the standard library of Vabi Elements, there are many constructions with materials ready that you can easily copy to your project.
Publications construction library
The constructions that are included by default in the Vabi Elements library are sourced from the following publications:
U- and R-Values of Building Constructions
U- and R- Values
Principles of Temperature Simulation Calculations, Physical Material Data
Thermal insulation of buildings – Calculation methods
Thermal insulation of buildings – Simplified calculation methods
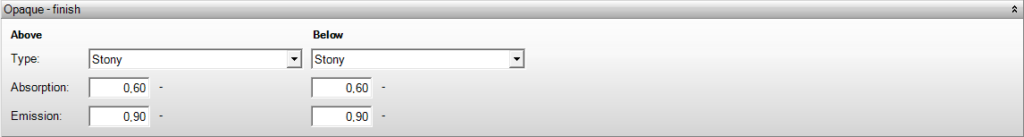
Finish
For floors, roofs, walls, panels, and doors, you can specify the finish for both the inside (interior) and outside (exterior) of the construction. It’s important to note that walls, panels, windows, and doors are defined using an inside and outside. Floors and roofs are defined based on top and bottom, regardless of whether it’s the inside or outside.
Type
- Warmteverlies
- Koellast
For the cooling load calculation, you need to specify a type to determine the departure mass. This type can only be specified when using “Rc and mass”. When using “material layers”, this input is determined automatically.
For the heat loss calculation, you need to indicate the type of construction to determine the surface warming allowance (ISSO 2012). These fields are not applicable for calculations according to ISSO 2017.
- Stony: A stony wall is a wall without cladding where there is no insulating layer with a lambda value <= 0.07 W/(m.K) on either side. This wall is fully considered for surface warming in the heat loss calculation.
- Stony with insulation covering: A stony wall with cladding is a wall where there is an insulating layer with a lambda value <= 0.07 W/(m.K) on the inside and/or outside. This wall is considered for 70% of its area for surface warming in the heat loss calculation.
- Not stony: A non-stony wall is not considered for surface warming in the heat loss calculation. In calculations according to ISSO 2017, these input fields do not serve any function.
Absorption
- Gebouwsimulatie
- Koellast
Absorption is the heat or cold that a surface of a construction can absorb in relation to its specific heat capacity. This property depends, for example, on the surface finish such as color and coating, and the type of material. Absorption applies to shortwave solar radiation. Emission concerns longwave radiation. Therefore, these do not necessarily have to be equal.
Publication
Absorption factors for opaque materials
Emission
- Gebouwsimulatie
Emission is the heat or cold that a surface of a construction can release to its surroundings in relation to its specific heat capacity. Emission concerns longwave radiation. Absorption applies to shortwave solar radiation. Therefore, absorption and emission do not need to be equal to each other. This property depends on the type of material. Metal surfaces generally have a lower value.
Material
Masonry
Paint (regardless of color)
Oxidized steel
Plain steel
Polished steel
0,91
0,88
0,79
0,35
0,26
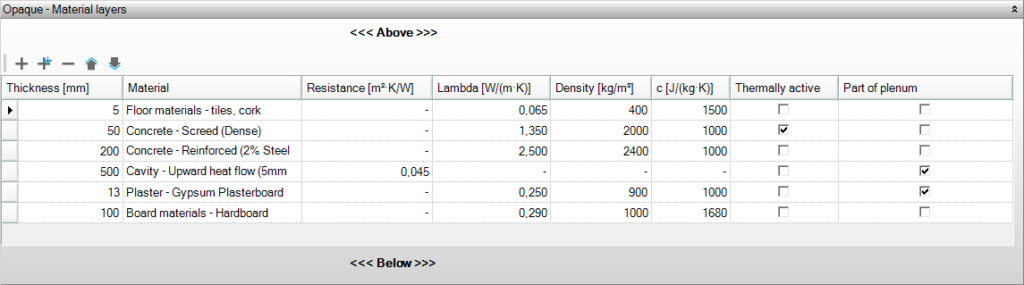
Material layers
It’s important to note that walls, panels, and doors are defined with an inside and outside. Floors and roofs are defined based on top and bottom, regardless of whether this refers to the inside or outside.
![]()
Add a layer of material, copy or delete it, and/or move material layers using the arrows.
Thickness
- Alle modules
Specify the thickness of the material layer in millimeters.
Material
- Alle modules
Choose one of the defined materials.
Thermally active
- Gebouwsimulatie
- Warmteverlies
When there is a heating/cooling device using a thermally active layer, indicate in which layer this device is located. This is necessary for the emission device floor heating, floor cooling, radiant ceiling, cooling ceiling, wall heating, or concrete core activation. A thermally active layer can only be located in a floor, roof, or wall.
Plenum
- Warmteverlies
Check the box if the material layer is part of the plenum. A plenum is the space between the ‘real’ ceiling and a suspended ceiling, as well as that between the ‘real’ floor and a raised floor, such as those used in computer rooms. This space is considered as the net volume of a room because air can circulate here. A plenum section can only be assigned to a floor or roof. The plenum is measured from the bottom of the plenum to the bottom of the floor above it.
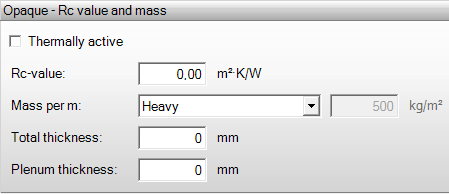
Rc value and mass
Thermally active
- Gebouwsimulatie
- Warmteverlies
Thermally active indicates which layer is the thermally active layer. This layer is then linked to the chosen emission template, provided that an emission device is assigned that uses the thermally active layer, such as underfloor heating, floor cooling, radiant ceiling, cooling ceiling, wall heating, or concrete core activation. A thermally active layer can only be located in a floor, roof, or wall.
Rc-value
- Gebouwsimulatie
- Warmteverlies
- Koellast
- EPG
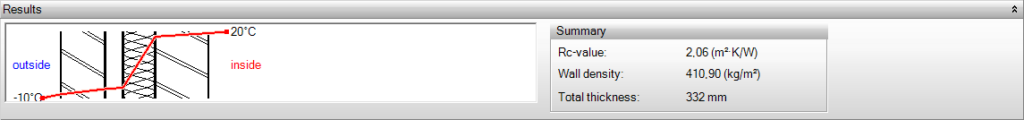
The Rc-value is the total thermal resistance of the construction. A well-insulated construction has the highest possible Rc-value.
Mass per m
- Gebouwsimulatie
- Warmteverlies
- Koellast
De massa is het gewicht van de constructie, uitgedrukt in vierkante meters.
- licht (100 kg/m²),
- gemiddeld (200 kg/m²),
- zwaar (500 kg/m²)
The mass per m is the weight of the construction, expressed in kilograms per square meter.
- Light (100 kg/m²)
- Medium (200 kg/m²)
- Heavy (500 kg/m²)
Publication
Building simulation
Specific mass, thermal conductivity coefficient, and specific heat
Total thickness
- Gebouwsimulatie
- Warmteverlies
- Koellast
- EPG
The total thickness of the construction is always important. The program includes wall thicknesses in the calculation of net floor areas and net volume.
Plenum thickness
- Warmteverlies
The plenum thickness is the thickness of the plenum. Plenum thickness is only entered for a floor or roof. The plenum indicates whether the material layer is part of the plenum. A plenum is the space between the “real” ceiling and a suspended ceiling, as well as between the “real” floor and a raised floor used in places like computer rooms. This space is considered as the net volume of a room, as air can circulate here. Plenum is only entered for a floor or roof. The plenum is measured from the bottom of the plenum to the bottom of the floor above it.
Air gap
Construction contains reflecting foil
- EPG
If a construction contains reflective foil, different heat transfer resistances are used, thereby improving the thermal insulation of a construction. Check the box if this is the case for floors, roofs, walls, panels, and doors.
Publication
Thermal insulation of buildings