Distribution hot domestic water
Multiple distribution systems for domestic hot water (EPG calculation) may be specified within the project. For example, consider a simple system including an electric water heater in the kitchen with a short pipe to the tap, or a circulation system with multiple hot water storage tanks. Only data regarding the possibly present (collective) circulation systems needs to be specified here because the distribution efficiency is partially combined with the emission efficiency for domestic hot water.
In the hot water distribution system, a generation configuration must be selected to provide the heat for the system. Only generation configurations with specified hot water generators will appear in the list; configurations without these will not be included.
Circulation System
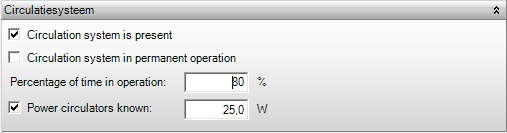
Circulation system is present
- EPG
This box indicates whether a circulation system is present in the building or part of the building. A circulation system can be specified only if the generation configuration is a collective system, which should be specified in the generation configuration for domestic hot water. The losses of the circulation system will be captured in the distribution efficiency, whereas the other energy losses are included in the emission efficiency, e.g. the losses in the pipes to the taps.
Circulation system in permanent operation
- EPG
This box indicates whether the circulation system in the building or part of the building is permanently in operation. If this is not the case, additional heat losses due to cooling are charged which are included in the distribution efficiency. By unchecking this box, an additional input field appears in which the percentage of time for which the circulation system is in operation can be indicated. Whether or not the circulation system is in permanent operation does not affect the calculations in case the flat rate method is applied to compute the distribution efficiency, see Pipe data.
Publications
Internal plus external distribution efficiency of the hot water system
Percentage van tijd in bedrijf
- EPG
The percentage of the day for which the circulation system is in operation can be indicated here if this system is not in permanent operation. This value does not affect the calculation results in case the flat rate method is applied to compute the distribution efficiency, see Pipe data.
Power circulators known
If the power of the circulators is known this should be specified here by checking the box; an additional input field then appears in which the power of the circulator can be expressed in W. Currently, it is required to specify the power of the pumps as the alternate method is not supported yet.
Publications
Electrical auxiliary energy use of circulation pumps
Pipe data
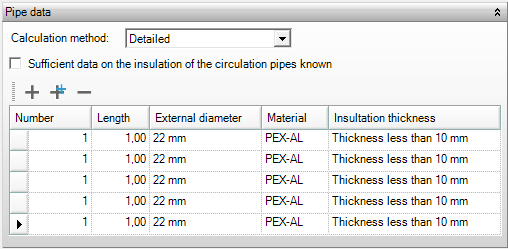
Calculation method
- EPG
The contribution of the pipes to the distribution efficiency may be computed with the flat rate or detailed method, which can be specified here. When choosing the flat rate method, only the insulation size for the system is required. If the detailed method is applied the pipes, materials, and insulation size for the system need to be specified.
- Flat rate
- Detailed
Publications
Internal plus external distribution efficiency of the hot water system – calculation values
Pipe insulation
- EPG
The pipe insulation needs to be specified if the calculation method for computing the distribution efficiency is flat rate. The pipe insulation determines the distribution efficiency as indicated in NEN 7120, Section 19.4.3.3.
- Uninsulated
- Minimum thickness of 10 mm
- Minimum thickness of 20 mm
Publications
Internal plus external distribution efficiency of the hot water system – calculation values
Detailed calculation method
- EPG
If the calculation method is chosen to be detailed, the above screen appears in which the piping of the circulation system can be specified. Pipes may be added, copied, and deleted using the icons in the screen.
Sufficient data on the insulation of the circulation pipes known
- EPG
With this box it can be indicated whether the data on the insulation of the circulation pipes is known, or whether it should be estimated, see Insulation thickness.
Number
- EPG
This number represents the number of identical pipes in the system. The length of the pipes is multiplied with this number and used as such in the calculations.
Length
- EPG
This represents the length of the pipe section, expressed in m.
External diameter
- EPG
The external diameter of the pipes should be specified as indicated in NEN 7120, Tables 19.4 and 19.6. The U-value per meter of copper pipe is determined using this external diameter in combination with the insulation thickness.
- 10 mm
- 12 mm
- 15 mm
- 22 mm
- 28 mm
- 35 mm
- 42 mm
- 54 mm
- 67 mm
- 80 mm
Publications
Internal plus external distribution efficiency of the hot water system – calculation values
Material
- EPG
The pipe material is specified here.
- Copper
- PE Polyethylene
- PEX PE with cross-links in the polymer structure
- PEX-Al PEX with an intermediate layer of aluminium
- PVC-C
- PPR Polypropylene
- PB Polybutylene
Publications
Internal plus external distribution efficiency of the hot water system – calculation values
Insulation Thickness (insufficient known data)
- EPG
When insufficient insulation data is available, the insulation thickness is specified according to NEN 7120, Table 19.6.
- Uninsulated
- Minimum thickness of 10 mm
- Minimum thickness of 20 mm
Publications
Internal plus external distribution efficiency of the hot water system – calculation values
Insulation Thickness (sufficient known data)
- EPG
When sufficient insulation data is available, the insulation thickness is specified according to NEN 7120, Table 19.4.
- Uninsulated
- 10 mm
- 15 mm
- 20 mm
- 25 mm